Electric Cars And Batteries: How Will The World Produce Enough
The age of the electric car is upon us. Earlier this year, the US automobile giant General Motors announced that it aims to stop selling petrol-powered and diesel models by 2035. Audi, based in Germany, plans to stop producing such vehicles by 2033. Many other automotive multinationals have issued similar road maps. Suddenly, major carmakers foot-dragging on electrifying their fleets is turning into a rush for the exit.
The electrification of personal mobility is picking up speed in a way that even its most ardent proponents might not have dreamt of just a few years ago. In many countries, government mandates will accelerate change. But even without new policies or regulations, half of global passenger-vehicle sales in 2035 will be electric, according to the BloombergNEF consultancy in London.
This massive industrial conversion marks a shift from a fuel-intensive to a material-intensive energy system, declared the International Energy Agency in May. In the coming decades, hundreds of millions of vehicles will hit the roads, carrying massive batteries inside them . And each of those batteries will contain tens of kilograms of materials that have yet to be mined.
The Need For Ev Battery Recycling
Lithium-ion batteries are the key component in an electric vehicleits most expensive component and the one that requires a supply chain of raw materials that can have human-rights and environmental costs. While electric vehicles emit no greenhouse gases during operation, the manufacturing process can contribute up to a quarter of the total global warming emissions in the life cycle of the vehicle. Most of the emissions come from the production of electricity to store in the battery, and the specific level of emissions from battery manufacturing is still uncertain.
Keeping lithium-ion batteries out of landfills is essential because of their toxicity and flammability. Recycling and reusing EV batteries can play a large role in reducing the need for lithium, cobalt, and nickel, and thus reduce the human and environmental costs of battery manufacturing and disposal.
Differences Between Electric And Conventional Car Batteries
The most common type of conventional car battery is the lead-acid battery. The technology behind the lead-acid battery is relatively ancient, dating back to 1859.
A Conventional 12-Volt Car Battery
The lithium-ion battery is much newer. A commercially viable lithium-ion battery didnt exist until the late 1990s.
Auto manufacturers use lithium-ion batteries in electric cars because theyre generally more efficient than lead-acid batteries, as well as less damaging to the environment.
Battery Pack of a Nissan Leaf EV
Compared to lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries charge faster, have a better weight-to-energy storage ratio and perform well even at extreme temperatures. Lithium-ion batteries also last much longer than lead-acid batteries. A lithium-ion battery can last as long as 10 years before needing replacement, while most lead-acid batteries will only work for three to five years.
The major downside to lithium-ion batteries is the cost of materials. At their most fundamental, lead-acid batteries are made up of lead plates and water mixed with sulfuric acid. Lithium-ion batteries need lithium to function. This metal is both expensive and most commonly harvested or mined from South Africa and the Andes, where conditions for workers can be significantly less safe than they are for miners in North America.
Don’t Miss: Are Car Lease Payments Tax Deductible
Can Electric Car Batteries Be Recycled
By: Kristen Hall-Geisler | Updated: Apr 15, 2021
Happily, the answer is yes — the batteries that power electric cars can be recycled. For decades, the few electric vehicles that were on the road were powered by lead-acid batteries. The latest models, with their lighter weight and longer range, use lithium-ion batteries, just like laptops and cell phones. In either case, the batteries that power electric cars can be recycled.
In the case of the older-technology lead-acid batteries, 96 percent of the materials in the battery — including the nasty lead — is recovered. To compare, only 38 percent of the material in glass bottles is recovered in the recycling process. They can also be recharged and reused before being recycled. Hybrid cars currently on the road, like the Toyota Prius, use nickel metal hydride batteries, which can be dismantled and recycled in much the same way.
When the battery packs in a lithium-ion-powered vehicle are deemed too worn out for driving, they still have up to 80 percent of their charge left. So before they ever get to a recycling center, these batteries are used to prop up the grid, especially alongside energy sources that may not be quite as steady, like wind or solar power. The batteries can store power to help the flow of electricity stay on an even keel rather than ebb and flow with the weather.
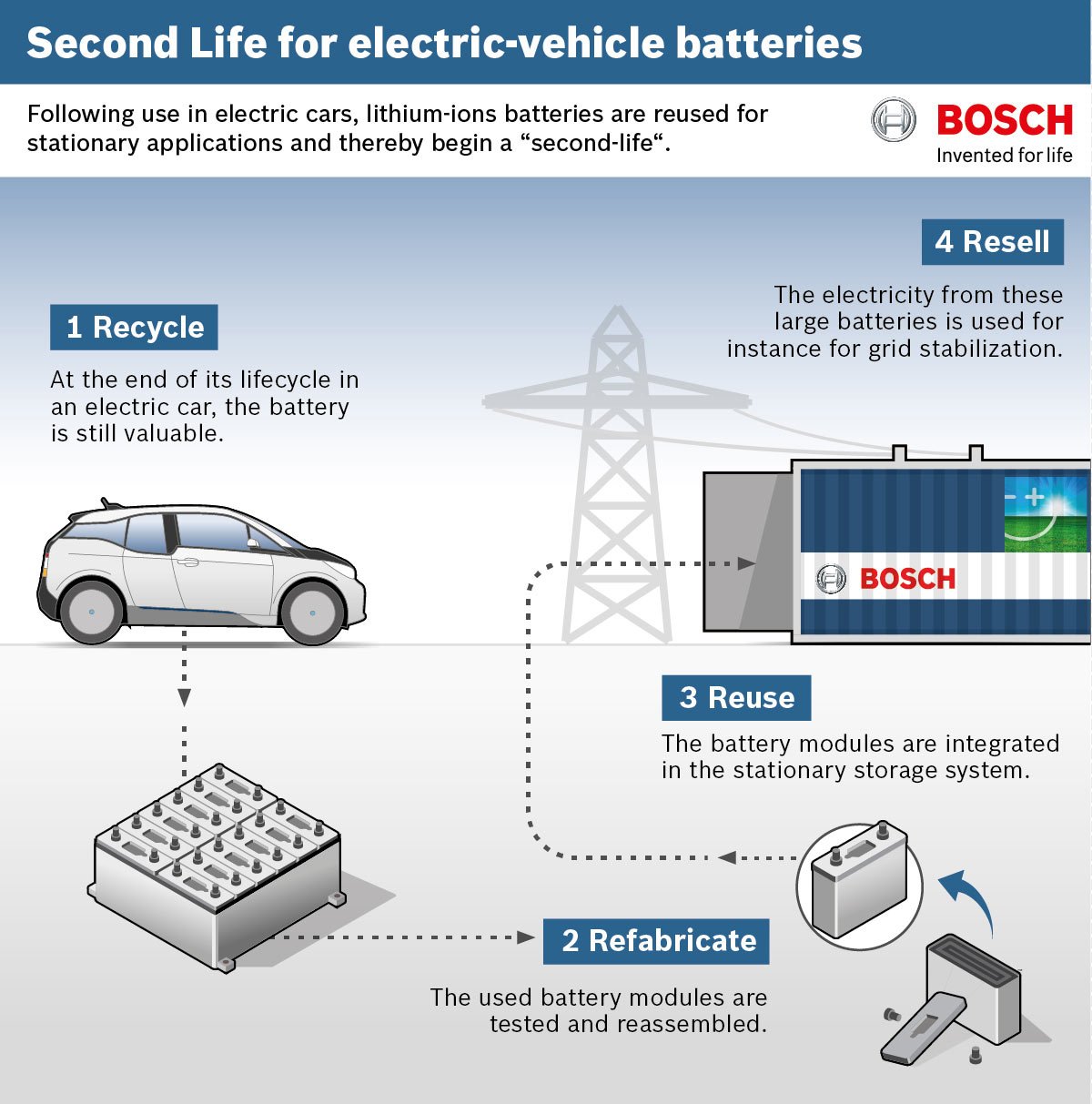
A Second Life For Electric Car Batteries

There are many examples of electric car batteries being given a second life when they are no longer suitable for their original purpose. Second life batteries are removed from the car, unpacked, graded and repurposed.
Amazingly, the battery pack in a 2019 Volkswagen e-Golf can store as much energy as a typical household consumes in one day.
For example, 280 Nissan Leaf batteries are used to provide back-up power to the Amsterdam Arena home of Ajax football club. Its Europes largest energy storage system powered by second-life electric car batteries and used by a commercial business.
In 2017, Renault and Powervault announced a partnership to reuse electric car batteries in home energy storage units. Meanwhile, in 2019, Volkswagen announced that it intended to use the battery packs from its electric vehicles in a network of portable charging stations. Each station can charge up to four vehicles at a time.
Also Check: How Much Does A Car Salesman Make Per Car
Reusing Batteries Across Industries
As the car example shows, the negative environmental effects of batteries are reduced as the battery lifetime extends. Electric batteries from vehicles can be repurposed and re-used in a different industry, thereby doubling the battery lifecycle to about 20 years.
When the capacity of electric car batteries drops below 70-80% after about 10 years of use, they are no longer strong enough to power the car. But they retain enough capacity for stationary storage in various contexts: in households, to balance power plants, or to electrify off-grid communities in rural areas.
However, re-purposing batteries is costly. This is due to limited information and data-sharing about the residual value of battery capacity, a lack of standards, and regulatory uncertainty about liability once the battery changes owners and applications. Overcoming these barriers requires cross-industry, public-private initiatives.
Battery Materials And Their Availability
Battery packs in EVs contain hundreds, even thousands, of individual lithium-ion batteries, typically referred to as cells and often similar in size to AA alkaline batteries. Cells consist of two electrodes: the anode and the cathode . When the battery is operating , lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through an electrolyte and a plastic separator that prevents the anode and cathode from coming into contact and short circuiting the cell. Electrons flow around the separator from the anode to the cathode through the device powered by the battery.
To facilitate smooth charging and discharging, battery packs consist of multiple cells bundled into modules. Combining several modules with additional packaging and thermal management systems creates the finished battery pack used in EVs.
Of the materials used in lithium-ion battery cells, the US government deems many to be critical . These elements are crucial to battery performance, yet their supply is at risk, whether due to material shortages or because supplies are concentrated or processed in a single country .
Different types of lithium-ion batteries are distinguished by the metals that make up the cathode. The choice of materials affects important battery characteristics such as longevity, cost, and energy density . The choice also affects other battery components, such as thermal and power management systems.
You May Like: How Car Salesmen Get Paid
Electric Car Battery Replacement Cost
When it comes to replacing an electric vehicle battery, you need not be too concerned as many manufacturers provide a warranty of up to 8 years or 100,000 miles. Meaning that even if you did need to replace it in an unfortunate event that something did go wrong, then it could well be covered under this warranty. Remember to always check the type of warranty offered by your chosen electric car manufacturer.
Also, the cost of batteries fell about 80% between 2010 and 2016 according to McKinsey, from $1000 to $227/kWh. Therefore, a new 40kWh battery in 2016 would have cost just shy of £10,000. Some predictions estimate that prices are set to fall below $100/kWh by 2030, around the same time as the government are aiming for 50% of all new vehicles sold in the UK will be electric.
Do Electric Vehicle Batteries Harm The Environment
As long as theyre recycled, then no- In fact, theyre likely to have a positive impact rather than a detrimental effect. Once their time as a car battery has come to an end, EV batteries can be recycled to power factories and households.
Repurposing EV batteries could result in a closed-loop recycling system. As a result, when the batteries life as a vehicle battery comes to an end, the factories that make them might be powered by the repurposed batteries. EV batteries have already been repurposed in other sectors by large car manufacturers.
Nissan, for example, proposes to repurpose EV batteries that have been retired to provide backup power to the Amsterdam ArenA, a world-famous entertainment arena and home to Ajax Football Club.
Don’t Miss: How Much To Get Car Detailed
New Recycling Techniques Set To Make Electric Vehicles Greener
A technician unpacks a completely burned Lithium-ion car battery before its dismantling by the German recycling firm Accurec in Krefeld, Germany, November 16, 2017. REUTERS/Wolfgang Rattay
- Robots could be used to speed up material separation
- Cost savings of 60% possible
- U.S., UK scientists focus on different technologies
LONDON, July 1 – Researchers in Britain and the United States have found ways to recycle electric vehicle batteries that can drastically cut costs and carbon emissions, shoring up sustainable supplies for an expected surge in demand.
The techniques, which involve retrieving parts of the battery so they can be reused, would help the auto industry tackle criticism that even though EVs reduce emissions over their lifetime, they start out with a heavy carbon footprint of mined materials.
As national governments and regions race to secure supplies for an expected acceleration in EV demand, the breakthroughs could make valuable supplies of materials such as cobalt and nickel go further. They would also reduce dependence on China and difficult mining jurisdictions.
“We can’t recycle complex products like batteries the way we recycle other metals. Shredding, mixing up the components of a battery and pyrometallurgy destroy value,” Gavin Harper, a research fellow at the government-backed Faraday Institution in Britain, said.
Pyrometallurgy refers to the extraction of metals using high heat in blast furnaces, which analysts say is not economic.
PROFITABLE RECYCLING
Life Cycle Analysis Comparison: Electric Vs Gasoline Vehicles
According to a report from the Union of Concerned Scientists, the production of a full-sized long-range electric vehicle adds about 6 tons of CO2 equivalent emissions, 68% higher than the production of a comparable gasoline car.
Most of these increased emissions come from battery manufacturing and resource extraction for the battery.
However, even with increased manufacturing emissions, the average EV is still better for the environment than a comparable gas car when you consider their lifetime CO2 eqiuvalent emissions in the United States .
Its important to note that a new gasoline car is greener than a new electric car out-of-the-lot. However, the longer you drive an EV, the more environmentally friendly it gets, because the increased manufacturing emissions are quickly offset by reduced emissions from driving on electricity instead of gasoline.
Overall, it takes about 19,000 miles of driving to offset the increased emissions from the production of an EV equivalent to the Tesla Model S. For smaller EVs like the Nissan Leaf, this time is even less .
More Details About the Report:
The report took into consideration every single aspect of an EVs life cycle, from the extraction of raw resources for manufacturing to the final disposal and recycling of the car.
The researchers assumed that both the full-sized electric vehicle and the comparable gas vehicle would have an approximate life expectancy of about 179,000 miles.
You May Like: What Oil Do I Need For My Car
Lithium And Ev Batteries:
Lithium is the 25th most abundant element. There is currently an oversupply of lithium on the market, driving prices down. However, some analysts predict a possible lithium shortage by 2050 as demand increases others forecast lithium supplies to last 50 years.
As demand for lithium grows, efforts are under way to develop additional sources in the U.S. as well as Australia. It is estimated that the lithium in Southern Californias Salton Sea could meet a third of the lithium demand today. Given the abundance of lithium and developments around its discovery and extraction, it seems unlikely that a shortage of lithium will make a shift to EVs impossible.
The Electric Car Market Is Booming: In 2018 The Global Fleet Exceeded 51 Million Vehicles And Is Expected To Reach 130 Million By 2030 According To The Global Ev Outlook 2019 This Trend Stems From The Desire To Reduce Diesel And Petrol Cars In Favour Of More Environmentally Friendly Electric Cars However The Composition Of Electric Cars Remains Problematic Mainly Because Of The Batteries Which Contain Pollutants Recycling Them Is Therefore A Major Challenge Through Sarp Industries And Its Subsidiary Euro Dieuze Industrie Which Specializes In The Treatment Of Batteries And Accumulators Veolia Offers Reliable And Appropriate Expertise
An electric car battery weighs an average of 300 kg but may be twice as much on some models. It is composed of plastics, solvents and electronics, but mainly of metals in the active part of the cell. Some of these metals are now becoming scarce: copper, cobalt, nickel, manganese, aluminium, lithium, etc. All may present a danger to the environment and human health.
Since 2006, European Directive 2006/66/EC has required 50% of the total weight of batteries to be recycled. Euro Dieuze Industrie, which handles more than 6,000 tonnes of batteries and accumulators per year, recycles up to 80% of them. The carbon extracted is recycled to make tyres, lubricants and additives, but can also be used by the metal industry to deoxidize metals. The recovered metals are resold in powder form for use in the production of alloys and chemical salts.
Who are our customers?
Recommended Reading: My Car Makes A Grinding Noise When I Accelerate
Demand For Battery Materials And The Role Of Recycling
The electrification of cars and trucks will need to accelerate to avoid the most severe impacts of global warming. By one estimate, the number of passenger BEVs on US roads could increase from roughly 1 million today to 43 million by 2035 and globally from 5 million to 245 million .3 Such growth will significantly increase demand for the minerals used in batteries. Accounting for projected changes in battery chemistry, global production of lithium, nickel, manganese, cobalt, and graphite for lithium-ion batteries across all end uses could increase five- to seventeen-fold over the next 20 years, depending on the material . This could strain the availability of these materials at todays levels of economically recoverable resources and manufacturing capacity.
The Role Of Batteries In Electric Vehicle Emissions
For conventional vehicles, their operation represents their largest contribution to global warming emissions. Roughly 90 percent of global warming emissions from combustion vehicles occur at the tailpipe. In contrast, all global warming emissions associated with BEVs occur upstream. That is, they come from manufacturing vehicles and generating electricity to power them.
Work by the Union of Concerned Scientists and others has found that, based on todays average sources of electricity in the United States, the total global warming emissions associated with BEVs are about 55 percent lower than those of gasoline vehicles. In parts of the country with higher levels of renewable energyCalifornia, for exampleBEVs reduce emissions by more than 70 percent. And the emissions associated with BEVs will continue to decline as the nation derives more of its electricity from renewable resources .
Upstream emissions from extracting and refining fuels and raw materials are also important considerations. For example, producing and processing crude oil into gasoline contributes an average of 24 percent of the fuels overall life cycle global warming emissions in the United States, depending on the source of the oil .
Read Also: Can You Lease A Car Through Carvana
What Happens To Those Big Batteries When They Reach Their End Of Life
- Wesleyan University, University of California, Berkeley
David Kuchta, Ph.D. has 10 years of experience in gardening and has read widely in environmental history and the energy transition. An environmental activist since the 1970s, he is also a historian, author, gardener, and educator.
There were some 11 million electric vehicles on the world’s roads in 2020, but by the end of the decade, that number could be 145 million., it could be 530 million. When those vehicles reach their end of life, there will be approximately 200,000 metric tons of lithium-ion batteries that need to be disposed of, recycled, or reused. How that will be done in an economical and sustainable manner is still to be determined.
The EV battery recycling industry is still in its infancy, since most EVs have been on the road fewer than five years, and their batteries may last two to three times longer than that. Much is still to be done in terms of research, standardization, and development. Without robust recycling, the world faces a highly toxic problem on its hands. With it, the environmental benefits of electric vehicles increase even more.
