The Anatomy Of A Car Engine
A V-6 Engine
Ill show you how the four-stroke engine works here in a bit, but before I do, I thought it would be helpful to go through the various parts of an engine so youll have an idea of whats doing what in the four-stroke process. There is terminology throughout these explanations that relies on other terms in the list, so dont worry if you get confused at first. Read through the whole thing to get an overall grasp, and then read it again so you have a basic understanding of each piece as its being talked about.
Engine Block
The engine block is the foundation of an engine. Most engine blocks are cast from an aluminum alloy, but iron is still used by some manufacturers. The engine block is also referred to as the cylinder block because of the big hole or tubes called cylinders that are cast into the integrated structure. The cylinder is where the engines pistons slide up and down. The more cylinders an engine has the more powerful it is. In addition to the cylinders, other ducts and passageways are built into the block that allow for oil and coolant to flow to different parts of the engine.
Combustion Chamber
Cylinder Head
Piston
Crankshaft
Along the crankshaft youll find balancing lobes that act as counterweights to balance the crankshaft and prevent engine damage from the wobbling that occurs when the crankshaft spins.
Camshaft
Timing System
Valvetrain
Valves
Rocker Arms
Pushrods/Lifters
Fuel Injectors
Sparkplug
How A Car Engine Works: Processes Inside The Engine Block
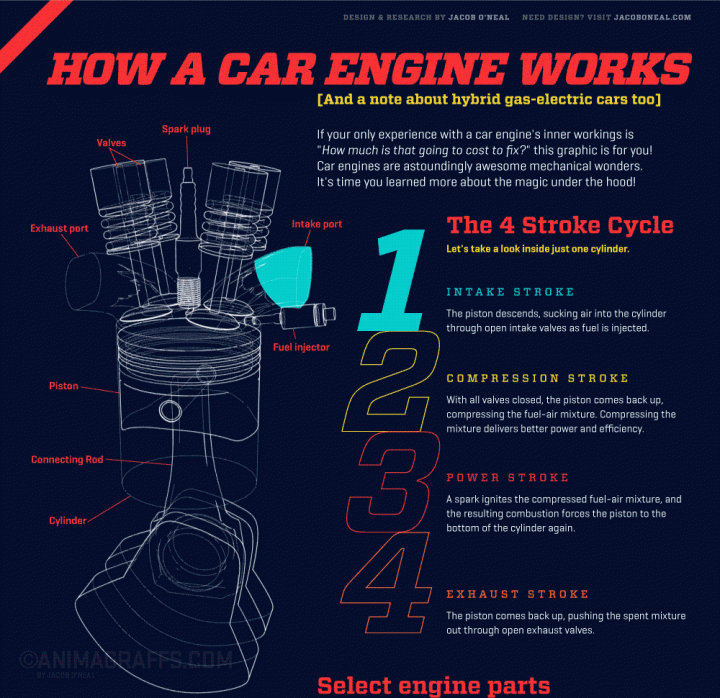
Now lets get started with the serious business, i.e. the combustion process. The combustion process takes place inside the combustion chamber present in the head. Here the most important part is the piston. The rotational force that is generated on the wheels starts with the movement of the piston. The piston generates usable power through a total of 4 strokes or 4 movements of the piston from end to end. Lets have a look at these 4 strokes in detail:
The 4 Strokes of the Engine:
1. Intake Stroke: The combustion starts with the piston at the top dead centre or TDC position. The piston now starts to move down. Just before the piston begins its downward motion, the intake valve opens up. As the piston moves down, it sucks in the fresh air-fuel mixture from the manifold. As the piston reaches bottom dead centre or BDC, the chamber fills up with air-fuel mixture.
2. Compression Stroke: Once the piston has reached BDC, the compression stroke begins. Just before the piston reaches the lowermost position, the intake valve closes. Now the piston moves upwards. As it moves up, it compresses the air-fuel mixture as it has no place to escape with the closed valves.
Also Read: Petrol vs Diesel Engine: The Differences Explained
Gif Courtesy:
A Brief History Of The Car Engine
The Internal Combustion Engine started as an experimental design created by a Dutch physicist around 1680. It was not until around 1859 that the first continuously operating ICE using spark-ignition was designed and tested successfully.
Although hailed as a significant achievement at the time, it took another 16 years to deliver a working four-stroke ICE. In 1885 Gottlieb Daimler designed and built the first modern ICE. It is a design that is still in use today. Most modern car engines are a direct descendant of this original design.
Read Also: How Much Does A Car Salesman Make Per Car
The Movement Of The Pistons Is Created In 4 Steps: Intake Compression Combustion And Exhaust
First, the piston is pulled down in the cylinder while the inlet valve injects a fuel and air mixture into the cylinder.
Second, the valve closes and the piston moves back up. This compresses the mixture to ready for ignition. After compression, the spark plug ignites.
The mini-explosion creates a hot gas that forces the piston back down which turns the crankshaft.
Finally, the force on the crankshaft powers the continued turning, forcing the piston back up. The outlet valve then opens releasing the exhaust from the cylinder.
The repetition of this process in each cylinder in rapid succession creates an enormous force that drives your vehicle forward.
How Big Do The Cylinders Need To Be
It’s not just how many cylinders a car has that’s important but how much power each one can make as it pushes out its piston. That depends on the size of the cylinder, which, in turn, depends on two key measurements: the diameter of the cylinder and how far the piston moves out . The area of a circle is × radius2, and since the bore is twice the radius, the useful volume of a car cylinder is × bore × bore × stroke. In physics terms, the volume of the cylinder is related to how much work the fuel does as it expands, how much energy it transfers to the piston, and , how much power the car makes. So the bore and stroke are very importantand that’s why they’re often quoted in technical specifications for car engines along with the number of cylinders. You’ll often see these measurements written in the form bore × stroke .
Artwork: How the bore, stroke, and displacement of one cylinder are measured. The bore is the diameter of the cylinder, the stroke is the distance the piston moves, and the displacement is the effective volume.
All of this is a bit of a generalization, because it’s easy to find examples of all types of cars that use square, oversquare, and undersquare engines, as the following table of engines past and present clearly shows.
| Bore | |
|---|---|
| 5343 | 12 |
Recommended Reading: How To Connect A Car Amp To A Wall Plug
How Does A Four
Watch this animation and you’ll see that a car engine makes itspowerby endlessly repeating a series of four steps :
The whole cycle then repeats itself.
The Four Strokes Of A Four
In today’s most modern engines, gasoline is injected directly into the cylinders near the top of the compression stroke. In either case, just before the piston reaches the top of its travel, known as top dead center, spark plugs ignite the air and fuel mixture.
The resulting expansion of hot, burning gases pushes the piston in the opposite direction during the combustion stroke. This is the stroke that gets the wheels on your car rolling, just like when you push down on the pedals of a bike. When the combustion stroke reaches bottom dead center, exhaust valves open to allow the combustion gases to get pumped out of the engine as the piston comes up again. When the exhaust is expelledit continues through the car’s exhaust system before exiting the back of the vehiclethe exhaust valves close at top dead center, and the whole process starts over again.
In a multicylinder car engine, the individual cylinders’ cycles are offset from each other and evenly spaced so that the combustion strokes do not occur simultaneously and so that the engine is as balanced and smooth as possible.
But not all engines are created equal. They come in many shapes and sizes. Most automobile engines arrange their cylinders in a straight line, such as an inline-four, or combine two banks of inline cylinders in a vee, as in a V-6 or a V-8. Engines are also classified by their size, or displacement, which is the combined volume of an engine’s cylinders.
Read Also: Car Salesman Commission
Whats The Crankshaft Doing
Its crucial to the smooth running of the engine. It is designed in such a way that the pistons, which are attached to it by connecting rods, dont all go up and down at the same time, but are staggered.
This way, each piston is at a different point in the four-stroke cycle, an arrangement that keeps all the parts of the engine turning smoothly. The crankshaft is also very strong because if it wasnt, the pistons might break away and burst out of the engine.
Different Types Of Car Engines
While all internal combustion engines generally work the same, there are several different types of engines. When discussing engines that most commonly appear in personal vehicles, the differences mainly have to do with how the cylinders are arranged. For instance, the cylinders of inline engines are lined up straight, while in V-style engines, the cylinders are separated into two groupings and form a V shape. Other engines will adjust certain mechanics such as the valve timing or the amount of air added to the four-stroke cycle to create more efficiency or power.
Knowing how a car engine works may prove helpful when its time to buy your next car, especially if youre getting it used from an individual instead of from a dealership. Learn how to buy a car from a private seller.
Also Check: How Much Does A Car Salesman Make On Commission
How Does The Car Engine Work
The basic operation of the car engine is pretty darn simple. Whether SI or CI the process that creates the power to drive the pistons involves multiple steps. These steps are intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
Sounds simple enough on the surface but lets drill down a bit more to see what is really going on:
How A Car Engine Works: The Fundamental Workflow
The modern day car engine is a 4-stroke engine which means it creates usable power in 4 strokes. Each stroke is defined as the movement of the piston from the bottom most position to the topmost position and vice-versa. The 4-strokes are as follows: Intake Stroke, Compression Stroke, Power Stroke, Exhaust Stroke. Here is a flowchart overview of the processes taking place from the start of the power cycle to the end:
You May Like: Why Do Car Windows Fog Up
How Does An Electric Car Work
Electric cars are making big waves in the automobile world. These noise-free, pollution-free and high-performance vehicles are expected to make their I.C. engine counterparts obsolete by 2025. In fact the first cars made were purely electrical. This article will unveil the hidden technologies behind the Tesla Model S, which recently became the worlds fastest accelerating production car. Tesla Model S P100D achieved 60mph speed in 2.28 seconds. We will see how electric cars have achieved superior performance by analyzing the technology behind the induction motor, inverter, lithium ion battery power source, and above all, the synchronized vehicle mechanism, in a logical, step-by-step manner.
Producing More Engine Power

Using all of this information, you can begin to see that there are lots of different ways to make an engine perform better. Car manufacturers are constantly playing with all of the following variables to make an engine more powerful and/or more fuel efficient.
Increase displacement: More displacement means more power because you can burn more gas during each revolution of the engine. You can increase displacement by making the cylinders bigger or by adding more cylinders. Twelve cylinders seems to be the practical limit.
Increase the compression ratio: Higher compression ratios produce more power, up to a point. The more you compress the air/fuel mixture, however, the more likely it is to spontaneously burst into flame . Higher-octane gasolines prevent this sort of early combustion. That is why high-performance cars generally need high-octane gasoline their engines are using higher compression ratios to get more power.
Stuff more into each cylinder: If you can cram more air into a cylinder of a given size, you can get more power from the cylinder without increasing the fuel required for combustion. Turbochargers and superchargers pressurize the incoming air to effectively cram more air into a cylinder.
Inject the fuel:Fuel injection allows very precise metering of fuel to each cylinder. This improves performance and fuel economy.
In the next sections, we’ll answer some common engine-related questions submitted by readers.
Don’t Miss: Adding Bluetooth To Factory Car Stereo
What Are The Pistons Doing While All This Is Going On
Weve left the pistons until last but in fact theyre the heart of the whole process. A car engine works on what is called the four-stroke combustion cycle. It was a principle invented by a German engineer called Nikolaus Otto in 1876, which is why its also called the Otto cycle.
The cycle begins with the piston at the top of its travel. In an engine with four valves per cylinder, the camshaft lobes push the inlet valves open.
As the piston starts to move back down the cylinder, it draws air through the open inlet orifices into the space between it and the top of the cylinder.
This is the intake stroke. At the same time, a small amount of fuel is squirted into the space by the injector.
Once the piston has reached its lowest point it rises back up, compressing the air and fuel mixture in the combustion chamber as it does so.
Just as it reaches the very top of its travel and point of maximum compression, the spark plug generates a spark, detonating the fuel mixture.
This forces the piston down once more. When it reaches the bottom of its stroke again, the exhaust valves open, allowing the hot gases to escape, and the whole cycle begins again.
How Do Hybrid Vehicle Engine Work
The classification above is defined by the ability of the electrical motor. In the following text, the different types of hybrid implementation in the terms of design will be discussed.
Three types of hybrid designs will be discussed, they are:
- Parallel hybrid
- Series-parallel hybrid
Parallel Hybrid
Imagine a car engine producing power and transferring that power to an axis which is, in turn, transferring that power to the wheels. On the other end, you have an electrical motor transferring its power to the same axis.
This is the basic principle of a parallel hybrid. Both the internal combustion engine and the electric motor send power to the same axis. In most cases, the electrical motor is between the engine and the transmission.
Series Hybrid
You may have heard of extended-range electric vehicles. They are hybrids that use both electric motor and an internal combustion engine.
The trick with series hybrids is that the engine is not connected to the wheels in any way. Instead, the engine is connected to a generator, supplying electricity for the electric motor.
The internal combustion engine turns on when there is no more charge in the battery, powering the electric motor directly. It can also be used to charge the battery.
Series-Parallel Hybrid
As the name suggests, the series-parallel hybrid combines both the design of the parallel hybrid and the series hybrid.
In other words, the internal combustion engine provides power to both the wheels and a generator.
Read Also: How Much Is Car Registration In Texas
Internal Combustion Engine Basics
Internal combustion engines provide outstanding drivability and durability, with more than 250 million highway transportation vehicles in the United States relying on them. Along with gasoline or diesel, they can also utilize renewable or alternative fuels . They can also be combined with hybrid electric powertrains to increase fuel economy or plug-in hybrid electric systems to extend the range of hybrid electric vehicles.
How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
Combustion, also known as burning, is the basic chemical process of releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture. In an internal combustion engine , the ignition and combustion of the fuel occurs within the engine itself. The engine then partially converts the energy from the combustion to work. The engine consists of a fixed cylinder and a moving piston. The expanding combustion gases push the piston, which in turn rotates the crankshaft. Ultimately, through a system of gears in the powertrain, this motion drives the vehicles wheels.
There are two kinds of internal combustion engines currently in production: the spark ignition gasoline engine and the compression ignition diesel engine. Most of these are four-stroke cycle engines, meaning four piston strokes are needed to complete a cycle. The cycle includes four distinct processes: intake, compression, combustion and power stroke, and exhaust.
Improving Combustion Engines
Types Of Car Engines: Layouts To Configurations
Turning a key or pressing a button is easy! Understanding whats going on under the hood gets a little more technical from types of car engines to cylinder configurations.
The tubes, wires, and weirdly shaped pipes all do their part to make your car go further faster. Lets take a look at:
- How Car Engines Work
- Cylinder Configurations
Also Check: How Much Is Car Registration In Texas
How Do I Know If My Car Engine Has A Problem
Sinceyour cars heart is dependent on many other systems to keep it healthy, we haveidentified the 8 most common problems that will contribute to heart failure:
