How Do Car Engines Work
Despite their relatively easy operation, cars are actually very complex machines. ;Cars need fuel to operate, but what does the engine actually do with it?
In general, a standard internal combustion engine what the majority of fuel-powered vehicles have today uses air combined with gasoline to produce power. Of course, it gets more complicated.
Different Types Of Car Engines
While all internal combustion engines generally work the same, there are several different types of engines. When discussing engines that most commonly appear in personal vehicles, the differences mainly have to do with how the cylinders are arranged. For instance, the cylinders of inline engines are lined up straight, while in V-style engines, the cylinders are separated into two groupings and form a V shape. Other engines will adjust certain mechanics such as the valve timing or the amount of air added to the four-stroke cycle to create more efficiency or power.
Knowing how a car engine works may prove helpful when its time to buy your next car, especially if youre getting it used from an individual instead of from a dealership. Learn how to buy a car from a private seller.
Engine Motion Is Cyclical
The first thing to remember is that engine motion is cyclical. Or at least that an engine generates momentum in its systems that helps to keep itself going. Its why when, for example, youre just about to stall your car, youre able to keep it going by either pressing down on the clutch pedal or by pressing the accelerator pedal. What youre doing with these actions is either reducing the load on the engine , or adding more fuel to the engine . Both of which help maintain the momentum.
Fundamentally, an engine converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which then rotates other parts of the engine through the use of belts.
Lets break down what these systems are.
Recommended Reading: Which Credit Cards Offer Rental Car Insurance
What Is A Car
That’s not quite such an obvious question as it seems. A car is ametal box with wheels at the corners that gets you from A to B, yes,but it’s more than that. In scientific terms, a car is anenergy converter: a machine that releases the energy locked in a fuel likegasoline or diesel and turns it into mechanical energy inmoving wheels and gears. When the wheels power the car, themechanical energy becomes kinetic energy: the energy that thecar and its occupants have as they go along. The challengeof building a car engine is to get as much energy out of each drop of fuel as possibleto makethe car go as far and as fast as it can.
Photo: Petroleum can be extracted from the groundby “nodding donkey” pumps like this one.Picture courtesy of US Department of Energy.
How A Car Engine Works
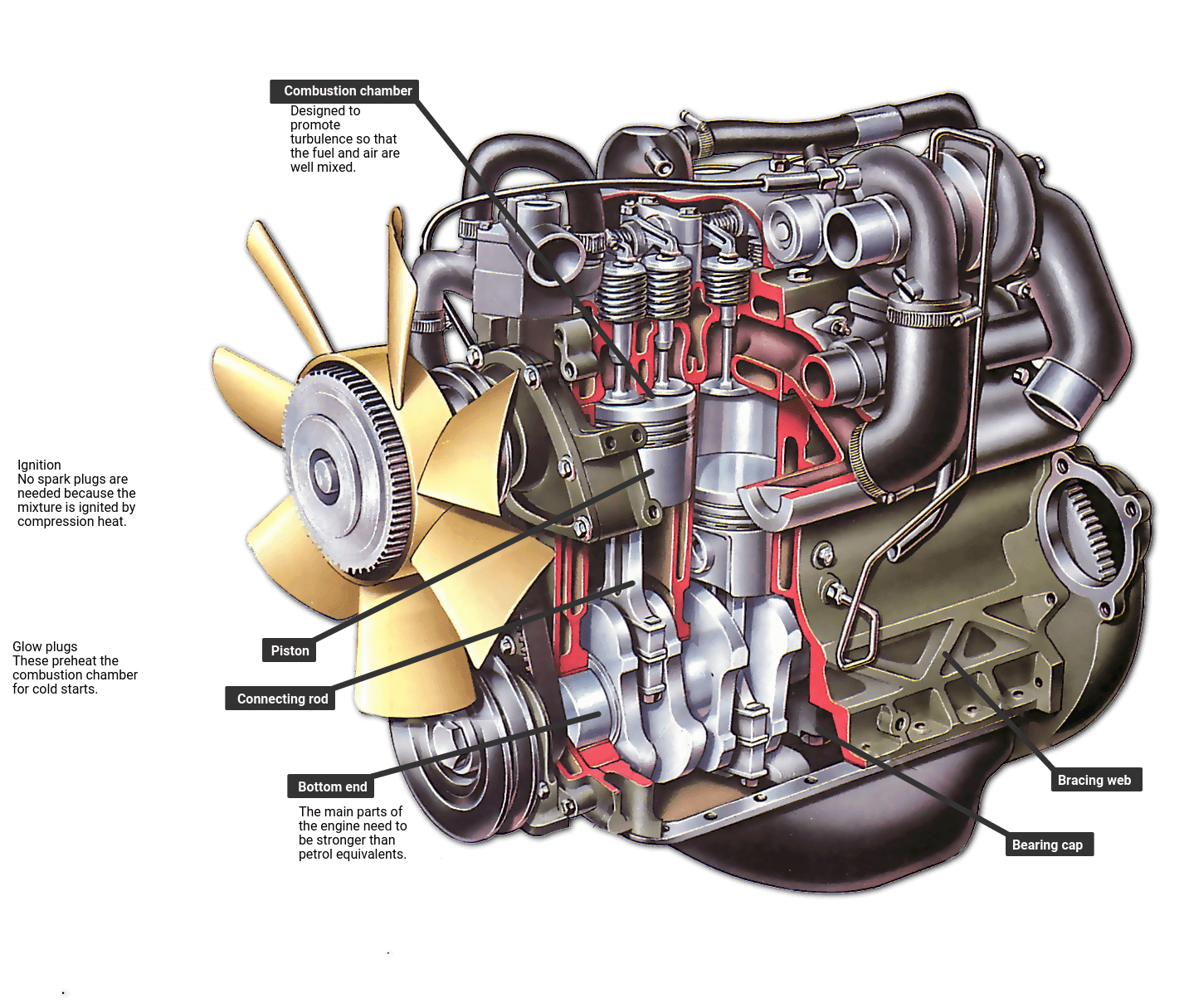
The car engine is the heartor perhaps rather the stomachof the car. In the engine, gasoline is burned to produce energy; this energy is then converted into motion. An engine has a number of components that work together to ensure this intricate piece of machinery continues to function smoothly.
First, there are the cylinders, in which gasoline is converted into energy, which is then harnessed to move the car.
Next, there are the valve train, which regulates the intake of fuel and the output of exhaust, and the ignition system, which insures that the spark plugs ignite the fuel in the cylinders at the correct time.
Engines also have a starting system, which consists of a separate, electric powered motor that is used to get the car going.
The cooling, exhaust, lubrication, and fuelsystems respectively make sure that the engine doesnt overheat; exhaust is filtered and released; all parts receive necessary oil; and the proper fuel mixture is injected into the engine.
Lets start with the cylinders.
Basically, a car engine is a kind of internal combustion engine. This essentially means that a fuel-air mixture is burnt inside a closed chamber in order to produce mechanical motion. In a car, this process occurs inside a cylinder.
The exhaust and intake camshafts are the two ovaloid shapes at the top of the cylinder. They regulate the opening of the valves.
The spark plug is the coil located between the two valves. The spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Rust On Car
The Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine is called an internal combustion engine because fuel and air combust inside the engine to create the energy to move the pistons, which in turn move the car .
Contrast that to an external combustion engine, where fuel is burned outside the engine and the energy created from that burning is what powers it. Steam engines are the best example of this. Coal is burned outside of the engine, which heats water to produce steam, which then powers the engine.
Most folks think that in the world of mechanized movement, steam-powered external combustion engines came before the internal combustion variety. The reality is that the internal combustion engine came first.
In the 16th century, inventors created a form of internal combustion engine using gunpowder as the fuel to power the movement of the pistons. Actually, it wasnt the gunpowder that moved them. The way this early internal combustion engine worked was youd stuff a piston all the way to the top of a cylinder and then ignite gunpowder beneath the piston. A vacuum would form after the explosion and suck the piston down the cylinder. Because this engine relied on the changes in air pressure to move the piston, they called it the atmospheric engine. It wasnt very efficient. By the 17th century, steam engines were showing a lot of promise, so the internal combustion engine was abandoned.
How Do The Air And Fuel Get Into The Combustion Chamber
Set into the top of the combustion chamber are, depending on the type of engine, two or four valves. Theyre slim discs of machined metal with a stem extending from them. When theyre in the closed position, they sit flush against the top of the combustion chamber.;
In an engine with four valves per cylinder , two of them are inlet valves that allow air into the combustion chamber, while the other two are exhaust valves, because they allow the hot gases to escape. The fuel is introduced by an injector set into the top of the combustion chamber that squirts it in just as the air enters.
You May Like: How To Match Car Paint
How Does A Petrol Engine Work
Petrol engines harness the energy created by petrol in the core of a car engine to propel the vehicle. Petrol is a high-energy fuel that releases large amounts of energy when ignited in an internal combustion engine.
Cars use a four-stroke combustion cycle, or Otto cycle, to convert gasoline into kinetic energy. The four strokes include the intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion stroke and exhaust stroke. The intake stroke starts the combustion process by allowing the engine to take in a cylinder-full of air and gasoline. After this process, air is compressed through the movement of the pistons in the engine. Upon compression, a spark plug emits a spark to ignite the gasoline and causes a controlled explosion in the cylinder. The resulting explosion causes the piston to move downward, which causes the exhaust valve to open and release exhaust out the tailpipe.
Petrol, also known as “crude oil,” consists of carbon and hydrogen atoms that split apart when burned. The combustion process in a petrol engine occurs when the carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen from the air to make carbon dioxide gas and water. Although the petrol engine revolutionized vehicular transport, experts claim it is the cause of pollution and global warming. As a result, hybrid cars that use a combination of electricity and gasoline power are becoming increasingly popular among environmentally-conscious drivers.
How A Car Engine Works: The 3 Main Parts
In broad terms, the engine can be segregated into three key parts, the head, the block and the oil sump.
1. The cylinder head is the channel through which the fuel enters the engine chamber and exhaust gases exit. Its key components are the camshafts, valves and spark plug.
2. The cylinder block is where all the combustion action takes place. The key components here are the combustion chamber, piston, and the crankshaft.
3. The oil sump constitutes the lowermost part of the engine. Its key components are the oil pan and the oil filter.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Car Do I Have
How Does A Car Engine Work
Bradley Jando | Tuesday 9th March 2021 4:02pm
The internal combustion engine is relied on by hundreds of millions of vehicles on a daily basis. Its a relatively efficient way of turning the energy stored in fuel into kinetic energy to help get cars moving. As its name suggests, it contains mini explosions, and turns the energy from those explosions into different forces. As were seeing now with electric cars, its not the only way to move a car but until quite recently its been the most efficient way of moving a car.
So how exactly does a car engine work?
What Is A Car Thermostat
The thermostat is one of the main components of an engine cooling system, serving to regulate the flow of coolant between the radiator and the engine.
While it may be small in size , the job it performs is crucial for your engine to stay within a safe operating temperature.
Too much heat for too long, and you can end up with a cracked engine block or blown head gasket .
You May Like: What Age To Stop Using Car Seat
How Car Engines Work
Have you ever opened the hood of your car and wondered what was going on in there? A car engine can look like a big confusing jumble of metal, tubes and wires to the uninitiated.
You might want to know what’s going on simply out of curiosity. Or perhaps you are buying a new car, and you hear things like “2.5-liter incline four” and “turbocharged” and “start/stop technology.” What does all of that mean?
In this article, we’ll discuss the basic idea behind an engine and then go into detail about how all the pieces fit together, what can go wrong and how to increase performance.
The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline is to burn the gasoline inside an engine. Therefore, a car engine is an internal combustion engine combustion takes place internally.
Two things to note:
- There are different kinds of internal combustion engines. Diesel engines are one type and gas turbine engines are another. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- There is also the external combustion engine. The steam engine in old-fashioned trains and steam boats is the best example of an external combustion engine. The fuel in a steam engine burns outside the engine to create steam, and the steam creates motion inside the engine. Internal combustion is a lot more efficient than external combustion, plus an internal combustion engine is a lot smaller.
The Wankel Or Rotary Engine
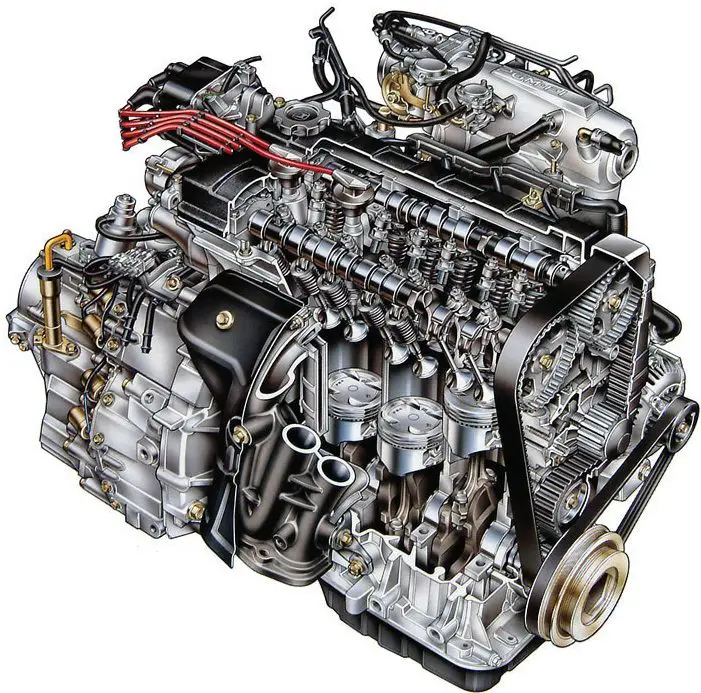

Prior to 2012, the Wankel engine proved to be one of the most innovative engine design configurations courtesy of Mazda. One of the most alluring things about the Wankel is that it comes with very few moving parts giving it a highly compact design. Unfortunately, it performed miserably in pollution and consumption norms so it never really did go beyond the Mazda platform. Instead of pistons, the Wankel utilized rotors to draw power from the combustion chamber. Additionally, instead of the crankshaft rotating, it was the entire cylinder block that actually moved around the crankshaft. An eccentric shaft is surrounded by a 3-sided symmetrical central rotor which allowed for greater efficiency since a single rotation of the rotor already accomplished the full 4 strokes of combustion engines.
The Wankel provided the following advantages.
- Exceptionally high ratio between power and weight
- Very few moving parts
- Simple design yet efficiently engineered
- Very refined
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Damage A Rental Car
Internal Combustion Engine Basics
Internal combustion engines provide outstanding drivability and durability, with more than 250 million highway transportation vehicles in the United States relying on them. Along with gasoline or diesel, they can also utilize renewable or alternative fuels .; They can also be combined with hybrid electric powertrains to increase fuel economy or plug-in hybrid electric systems to extend the range of;hybrid electric vehicles.
How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
Combustion, also known as burning, is the basic chemical process of releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture.; In an internal combustion engine , the ignition and combustion of the fuel occurs within the engine itself. The engine then partially converts the energy from the combustion to work. The engine consists of a fixed cylinder and a moving piston. The expanding combustion gases push the piston, which in turn rotates the crankshaft. Ultimately, through a system of gears in the powertrain, this motion drives the vehicles wheels.
There are two kinds of internal combustion engines currently in production: the spark ignition gasoline engine and the compression ignition diesel engine. Most of these are four-stroke cycle engines, meaning four piston strokes are needed to complete a cycle. The cycle includes four distinct processes: intake, compression, combustion and power stroke, and exhaust.
Improving Combustion Engines
How A Car Engine Works: The Processes Inside The Engine Head
The combustion process begins at the engine head, precisely at the intake manifold. The intake manifold is the channel through which the air-fuel mixture flows into the combustion chamber. The air is directly sucked into the manifold from the throttle body. The fuel, on the other hand, is injected into the end of the manifold through a nozzle called the fuel injector.
Next, we move on to the tap controlling the fuel release, the valve. The valve in simple terms is the device that seals the chamber shut during combustion and opens the gate when fuel has to enter the chamber or gases have to exit. The valves open and close based on which stroke is taking place. The opening and closing of the valves are done by an actuator rod known as the camshaft.
The camshaft is a cylindrical rod with drop shaped protrusions known as cams. When the sharp end of the cam is rotating against the valve, it pushes the valve downwards and opens up the port. Once the sharp end transitions back to the round end, the valve springs push back the valve to its original position and shut the port. The rotation of the camshaft is connected to the rotation of the crankshaft via belts and pulleys. The rotation is timed with a very delicate and precise timing mechanism that can be adjusted manually.
Video Courtesy:
Don’t Miss: What To Use To Clean Car Windows
What Causes The Explosions
In a petrol-powered engine theyre caused by spark plugs . When an electrical charge is passed through them, they generate a spark that ignites a mixture of petrol and air.;
This all takes place in the combustion chamber, a small space between the top of the piston and the cylinder. The cylinder is what the piston moves up and down in. Engines are often known by the number of cylinders they have. A four-cylinder engine, with the cylinders arranged in a line, is the most common.;
The hot gases produced by the spark plug igniting the fuel-air mixture rapidly expand inside the combustion chamber, pushing the piston down the cylinder.;
In a diesel-powered engine there are no spark plugs. Instead, the explosion is caused by the piston compressing the air in the combustion chamber to such a degree that it gets very hot. At that point, diesel is squirted into it and spontaneously ignites, causing an explosion which, again, forces the piston down.;
How A Car Engine Works: Processes Inside The Engine Block
Now lets get started with the serious business, i.e. the combustion process. The combustion process takes place inside the combustion chamber present in the head. Here the most important part is the piston. The rotational force that is generated on the wheels starts with the movement of the piston. The piston generates usable power through a total of 4 strokes or 4 movements of the piston from end to end. Lets have a look at these 4 strokes in detail:
The 4 Strokes of the Engine:
1. Intake Stroke: The combustion starts with the piston at the top dead centre or TDC position. The piston now starts to move down. Just before the piston begins its downward motion, the intake valve opens up. As the piston moves down, it sucks in the fresh air-fuel mixture from the manifold. As the piston reaches bottom dead centre or BDC, the chamber fills up with air-fuel mixture.
2. Compression Stroke: Once the piston has reached BDC, the compression stroke begins. Just before the piston reaches the lowermost position, the intake valve closes. Now the piston moves upwards. As it moves up, it compresses the air-fuel mixture as it has no place to escape with the closed valves.
Also Read: Petrol vs Diesel Engine: The Differences Explained
Gif Courtesy:
Don’t Miss: What Do You Need To Get Your Car Inspected
The Inline Or Straight
As the term implies, the arrangement of the cylinders are in a pretty straightforward linear fashion. Most cars today use this configuration for a variety of reasons. The cylinders are located directly above the crankshaft. Examples of these are the ubiquitous inline-4 and the more European standard straight-6. As you have guessed it, an inline-4 will have 4 cylinders arranged in a straight line. A straight six will have 6 cylinders. Audi and BMW are fanatics when it comes to the straight-6.
The advantages of a straight or inline configuration include the following:
- Compact and lightweight
- Ideal for modern front-wheel drive cars
- Easily tunable
The straight or inline layout does have caveats, though.
- Limited maximum size
- Less rigid than other engine configurations
